Updating the FITS File
Updating each science image with the distortion model using this merged convention requires integrating these new reference files directly into the FITS file. This update gets performed using the following steps:
determining what reference files should be applied to the science image
read in distortion coefficients from IDCTAB reference file
[for ACS data only] compute time-dependent (TDD) skew terms from model described in IDCTAB file
read in velocity aberration correction factor (VAFACTOR) keyword
apply velocity aberration, and the TDD terms for ACS data as well, to the distortion coefficients
write time-corrected distortion coefficients as the SIP keywords
[if d2imfile is to be applied] read in D2IMFILE reference table
update D2IMEXT with name of reference table and AXISCORR keyword with axis to be corrected
append D2IMFILE array as a new
D2IMARRextension
[if NPOLFILE is to be applied] divide the NPOLFILE arrays by the linear distortion coefficients
write out normalized NPOLFILE arrays as new
WCSDVARRextensionsupdate each SCI extension in the science image with the record-value keywords to point to the 2
WCSDVARRextensions (one for X corrections, one for Y corrections) associated with the SCI extension’s chip
The STWCS task updatewcs applies these steps to update a science image’s FITS file to incorporate the distortion model components using this convention. It not only modifies the input reference file data to apply to each image to account for time-dependent and velocity-aberration corrections as needed, but also creates the new extensions which get appended to the science image’s FITS file.
Creating the D2IMARR extension
Converting the D2IMFILE reference table into a new D2IMARR FITS image extension involves only a few simple revisions
to the header from D2IMFILE. The header of the D2IMARR extension consists of the following keywords required in order to
properly interpret and apply the data in the extension to the science array:
AXISCORR : Direction in which the det2im correction is applied
EXTNAME : Set to ‘D2IMARR’
EXTVER : Set to 1
NAXIS : Number of axes
NAXISj: Size of each axisCRPIXj: Reference point for each axis, set at axis centerCRVALj: computed from input science image array center on chipCDELTj: Binning of axis, computed as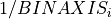 keyword from science image
keyword from science image
These keywords supplement the standard FITS required keywords for an image extension, including such keywords as PCOUNT, GCOUNT, BITPIX, and XTENSION.
The corrections specified in this extension refer to pixel positions on the detector. Since science images can be taken both as subarrays and in binned modes for some instruments, the subarray offset and binning factor get used to compute the translation from science image pixel position into unbinned full-detector pixel positions. Subarray exposures taken by HST detectors record the position of the detector’s origin, (0,0) pixel, as LTVj keywords to identify what pixels on the physical detector were read out for the exposure. The conversion factor from image pixel position to physical detector pixel position of (NAXISj/2 + LTVj)*BINAXISj gets recorded as the CRVALj keyword value and gets used to correctly apply this correction to the science image.
In addition to the pixel position transformations encoded as the D2IMARR WCS, keywords reporting how the D2IM correction was created get copied into the new D2IMARR image extension header from the primary header of the D2IMFILE. This maintains as much provenance as possible for this correction.
A full listing of the D2IMARR extension for a sample ACS image can be found in D2IMARR Header in Appendix 1: Headerlet API.
Creating the WCSDVARR Extension
The NPOLFILE reference file contains at least 2 image extensions, one for the X correction and one for the Y correction for each chip. All these extensions get converted into their own WCSDVARR extension based on the FITS Distortion Paper convention when the NPOLFILE gets incorporated into the science image as another component of the distortion model. Both the array data for each NPOLFILE extension and the corresponding header needs to be modified before it can be written into the science image FITS file as a new WCSDVARR image extension.
The data from the NPOLFILE arrays represent the residuals after accounting for the distortion model, yet this correction gets applied as part of the distortion correction described in Equation 4. The linear terms of the distortion model need to be removed from the data in each NPOLFILE array in order to avoid applying the linear terms twice when applying the correction to the science data. This gets performed by reading in the linear distortion coefficients directly from the OCX and OCY keywords written out along with the SIP keywords, the multiplying them into the NPOLFILE data values using matrix dot operator to get the final, image specific NPOL correction to be written out as the WCSDVARR extension.
The header of this new WCSDVARR extension provides the translation from science image pixels to NPOLFILE array pixel positions as well as reporting on the provenance of the calibrations as recorded in the original NPOLFILE. The following keywords get computed based on the values directly from the NPOLFILE header:
NAXISj: Length of each axisCDELTj: Step size in detector pixels along each axis for the NPOL arrayCRPIXj: Reference pixel position of NPOL arrayCRVALj: Reference pixel position of NPOL array relative to science arrayEXTNAME : always set to WCSDVARR
EXTVER : identifier reported in the DP.EXTVER record-value keywords in the science array header
These keywords supplement the standard FITS required keywords for an image extension, including such keywords as PCOUNT, GCOUNT, BITPIX, and XTENSION. In addition, all keywords from the NPOLFILE primary header after and including ‘FILENAME’ get copied into the header of each WCSDARR extension to preserve the provenance of the calibration.
The look-up tables are saved as separate FITS image extensions in the science files with EXTNAME
set to WCSDVARR. EXTVER is used when more than one look-up table is present in a single science
file. Software which performs coordinate transformation will use bilinear interpolation to get
the value of the distortion at a certain location in the image array. To fully map the image
array to the distortion array the standard WCS keywords CRPIXj, CRVALj and CDELTj are used. The
mapping follows the transformation
(1)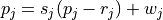
where 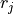 is the
is the CRPIXj value in the distortion array which
corresponds to the 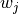 value in the image array, recorded as
value in the image array, recorded as
CRVALj in the WCSDVARR header. Elements in the distortion array are spaced
by 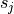 pixels in the image array, where
pixels in the image array, where 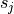 is the
is the CDELTj
value in the distortion array header. In general 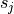 can have
a non-integer value but cannot be zero. However, if the distortion array
was obtained as a subimage of a larger array having a non-integer step size
can produce undesirable results during interpolation. A full listing of the
can have
a non-integer value but cannot be zero. However, if the distortion array
was obtained as a subimage of a larger array having a non-integer step size
can produce undesirable results during interpolation. A full listing of the
WCSDVARR extension for a sample ACS image can be found in WCSDVARR Header in Appendix 1: Headerlet API.